Data Governance Operating Model
A data governance operating model is a an operating model that defines an organization's key data processes, the roles and tasks involved in each of those processes, and the people, tools, and technology that are required to fulfill each of the processes.
In this section:
- We outline the data goals for GBADs
- We outline the data governance operating model for GBADs using the GBADs' governance structure (Working Groups) to understand the roles and responsibilities for each of the tasks involved to fulfill the data goals
Goals
The main data goals for GBADs can be broken down into the following:
General
Data Goal 1. Access to technology and products that are innovative and advance the state-of-the-art.
Data
Data Goal 2. Identify data sources that are required for GBADs modelling purposes
- When necessary, create data allicances with private and public data holders
Data Goal 3. Data is accessible for users (both humans and machines) and can be used in a timely matter for decision making [^1]
- This includes data that GBADs redirects from other organizations and data that GBADs stores for associated projects and partners [^1].
Data Goal 4. Data have been analyzed for quality, and these metrics are available as part of the metadata [^1]
Data Goal 5. Data is cleaned only once - reduce replication of data sources and cleaning
Data Goal 6. Data is findable to data users [^1]
Data Goal 7. A system that allows for the customization of information through mechanisms and processing that adjusts the granularity of the data to the user's needs[^1]
Data Goal 8. Data that are interpretable—the semantics to be encoded in meta-data and other semantic systems [^1]
Models and Data Visualizations
Data Goal 9. Modelling procedures are reproducible
Data Goal 10. Data lineage is traced to ensure that all data procedures are replicable, to ensure that data is not replicated, to help with data quality and updates, and to keep track of which versions of data are used in publications
Data Goal 11. Data visualizations and dashboards are served on GBADs servers, use data from the GBADs Knowledge Engine (GBADs data sources), and link to metadata and methods
Data governance procedures and processes are crucial to fulfill the goals, to create a system that is FAIR(S), and to ensure that data processes, publications, and models are reproducible. Each goal has its own processes that require unique technological tools and individual (human) responsibilities from the Informatics theme, and others using and creating data models in GBADs. The GBADs governance structure (Working Groups) provide a vantage point for understanding where responsibility lies in the data governance operating structure.
People and Processes - GBADs Working Groups
GBADs is split into three main Working Groups, each with unique, but overlapping responsibilities. Working Groups are organized with each building on each other, where the data lies as the backbone structure (Figure 1).
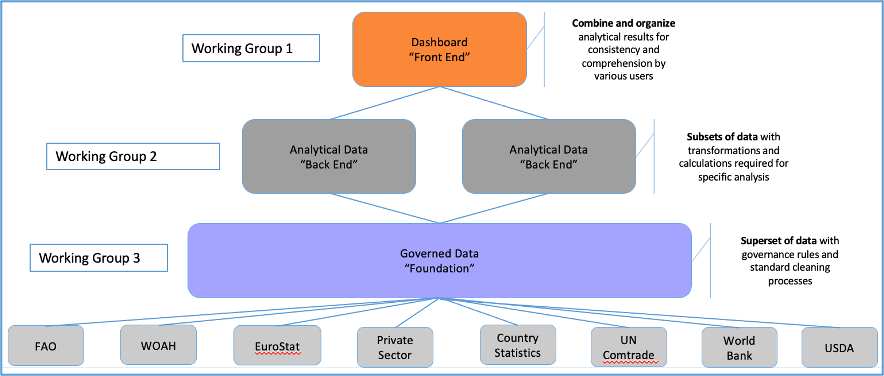 Figure 1: GBADs Working Groups
Figure 1: GBADs Working Groups
Each working group has a set of responsibilities as outlined by GBADs to fulfill the goal of estimating the economic and health burden of animal diseases through modelling efforts. The responsibilities outlined overlap with the GBADs data goals through interactions with obtaining, using, and managing data. The table below outlines the description of responsibilities for each working group and which goals pertain to each working group:
| Working Group | Description of Responsibilities[^2] | Overlap with Goals |
|---|---|---|
| Working Group 1 (WG1) - Data alliances, Communication of information and Adoption and uptake |
| |
| Working Group 2 (WG2) Methods and Analytics |
| |
| Working Group 3 (WG3) - Informatics |
|
The data governance operating model uses the working group structure to allocate roles and responsibilities related to the data goals.
References:
[^1] https://acsess.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/agj2.21017?af=R [^2] Working groups and description of responsibilites taken from the GBADs Bill and Melinda Gates Investment Document 2022 [^3] https://tdan.com/the-non-invasive-data-governanceo-operating-model/12210